Agentic AI is reshaping how digital systems think, act, and make decisions.
Unlike traditional AI models that respond passively to a prompt, agentic AI can independently plan tasks, take actions across tools, and refine its approach through feedback. This autonomy creates revolutionary opportunities—but it also introduces new and far more complex fraud risks. As attackers adopt agentic AI to scale operations and mimic human behavior with precision, businesses must evolve their defenses accordingly.
This article explains the mechanics behind agentic AI, how it supercharges modern fraud techniques, and the defensive strategies—including adaptive verification and device trust—that organizations must implement to stay resilient.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems capable of autonomous decision-making and multi-step execution. Instead of simply generating text, an agent can:
- Break down a task into smaller steps (planning)
- Use APIs, browsers, or tools to take action (acting)
- Evaluate outcomes and adjust next steps (reflection)
- Seamlessly integrate external systems (tool use)
These capabilities make agentic AI function more like a digital worker—proactive, persistent, and adaptive.
Why Agentic AI Is Transformative for Business
Agentic AI unlocks significant value across industries. Businesses use it to:
- Automate complex workflows
- Enhance customer support
- Generate content, reports, and code
- Improve operational efficiency
- Coordinate multi-agent collaboration
The potential is enormous: faster output, lower cost, and scalable decision-making. However, the same strengths—speed, autonomy, and adaptability—can also be weaponized.
The Dark Side: How Agentic AI Enables New Fraud Threats
1. Autonomous Accounts Abuse
How it works: Agentic AI can independently run multi-step account workflows—registering accounts, verifying emails, rotating identities, solving challenges, and reattempting failed steps. This turns account creation fraud (ACF) and account takeover (ATO) into continuous, self-optimizing pipelines.
Professional fraud types: Credential stuffing automation, account farming, new account fraud (NAF), identity cycling, multi-step ATO.
2. Sophisticated Transaction & Payment Fraud
How it works: Unlike scripted bots, agentic agents can dynamically navigate checkout flows, retry declined cards, adjust purchase patterns, and mimic legitimate timing to evade detection. This enables highly efficient card testing and transaction fraud across e-commerce systems.
Professional fraud types: Card testing fraud, triangulation fraud, checkout abuse, automated refund abuse, payment orchestration misuse.
3. Scalable Abuse of Online Systems
How it works: Agentic AI evaluates page structures, evades anti-scraping rules, and coordinates multi-agent actions to target high-value products or data sources. This results in industrial-scale scalping operations or scraping attacks that adapt instantly to UI or logic changes.
Professional fraud types: Inventory hoarding, bot-driven scalping, scraping-as-a-service, price monitoring abuse, product availability manipulation.
4. AI-Enhanced Identity and Content Fraud
How it works: Agents can generate synthetic identities, falsified documents, and contextually relevant responses to pass weak onboarding or KYC processes. They automatically resubmit variations until a verification loophole is found.
Professional fraud types: Synthetic identity fraud, deepfake KYC bypass, document tampering automation, impersonation-as-a-service.
5. Agent Hijacking & Tool-Chain Exploitation
How it works: Because agentic systems rely on tool-chaining and autonomous execution, attackers can manipulate agent instructions to execute unauthorized workflows—such as issuing refunds, exporting data, or triggering internal APIs.
Professional fraud types: Prompt injection fraud, autonomous API exploitation, unauthorized workflow execution, machine identity compromise.
Why Traditional Security Fails Against Agentic AI
Traditional fraud prevention relies on static rules, traditional CAPTCHA, basic device checks, and human behavior baselines. Agentic AI extends the traditional AI agent, breaking these assumptions:
- It learns and adapts faster than static defenses
- It mimics human behavior convincingly
- It rotates devices, IPs, and environments programmatically
- It automates attacks that older systems expect from humans
Legacy anti-bot solutions, rule-only systems, and simple behavioral models cannot keep pace with autonomous, tool-using, self-correcting agents.
How To Protect Against Agentic-AI-Driven Fraud
Protecting against agentic-AI-driven fraud requires layered, adaptive, and intelligence-driven defenses that directly disrupt autonomous agents while maintaining a legitimate user experience. Key strategies include:
1. Adaptive Verification
Dynamic verification challenges prevent autonomous agents from completing tasks without interruption. Continuously changing challenges—such as puzzles, click, or drag interactions—break automated workflows and make it extremely difficult for agents to reuse learned patterns. This disrupts multi-step attacks like automated account creation, credential stuffing, and bot-driven checkout processes.
2. Device Fingerprinting and Trust
Detailed device and environment profiling identifies hallmarks of agentic AI abuse, such as emulators, virtual machines, browser spoofing, and rapid device rotation. By establishing device reputation scores, legitimate users can pass with minimal friction, while suspicious devices face escalated verification. This prevents AI-driven attacks from exploiting high-trust channels or executing repeated abuse cycles.
3. Multi-Signal Behavior and Risk Analysis
Monitoring interaction patterns across devices, sessions, and IP addresses allows detection of automation signatures, including ultra-fast task execution, multi-step sequences, or coordinated agent workflows. Suspicious activity is challenged or blocked in real time, mitigating threats such as account takeover, automated card testing, scalping, and synthetic identity fraud.
4. Identity and Session Controls
Enforcing multi-factor authentication, passkeys, token binding, and scoped session permissions limits the potential impact of compromised agents. Autonomous workflows cannot hijack accounts or escalate privileges without triggering verification or access restrictions, protecting against unauthorized transactions and internal system abuse.
5. API and Workflow Protection
Implementing rate limits, signed requests, and anomaly detection prevents agents from abusing backend workflows, such as automated refund operations, mass data exports, or multi-step transaction orchestration. Even if an agent bypasses front-end defenses, these controls ensure automated actions cannot compromise system integrity.
Agentic AI Fraud Solutions: GeeTest Defense Framework
To counter autonomous, self-improving, multi-step AI attacks, GeeTest strengthens the entire user journey with layered protections engineered specifically for agentic fraud behaviors:
GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA
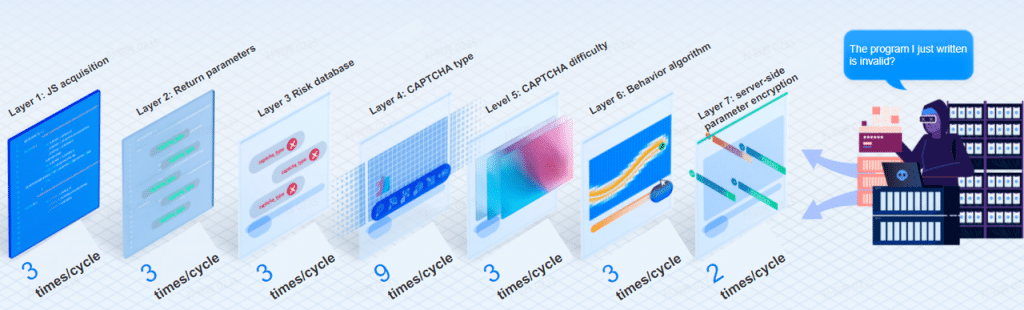
- Disrupts automated workflows by combining seven-layer dynamic verification with multiple challenge modes.
- Uses continuous AI-driven resource updates (up to 300,000 images/hour) to invalidate learned agentic AI models.
- Automatically adapts challenge intensity based on risk, protecting against account farming, card testing, checkout bots, and multi-step attack sequences.
GeeTest Device Fingerprinting
- Detects emulators, VM usage, rapid device switching, and browser spoofing, exposing AI-driven automation.
- Fraud detection through device and behavioral risk analysis.
- Seamless trust evaluation enabling lower friction for legitimate users
Business Rules Decision Engine
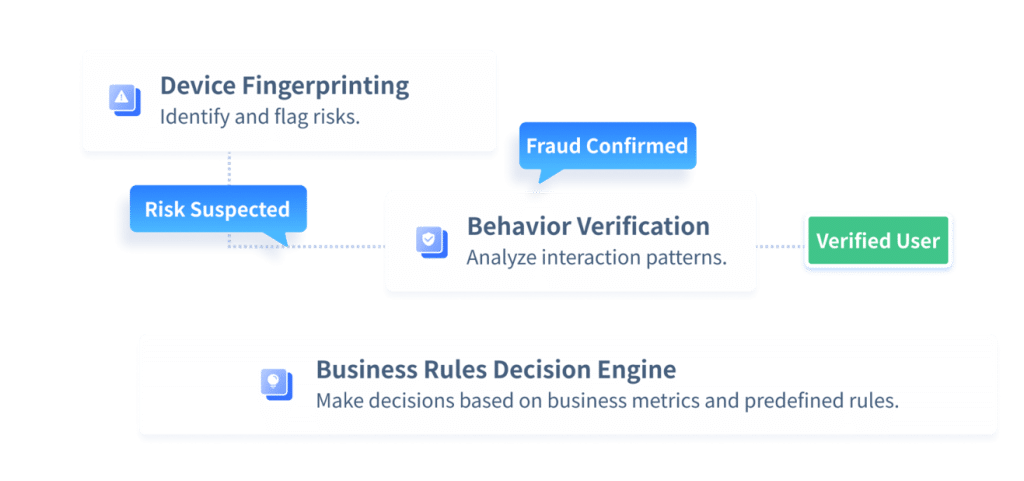
- Aggregates signals from business and existing risk control systems, such as device intelligence, interaction patterns, IP, geography, and transaction context.
- Update business rules dynamically without service downtime or coding, ensuring fast adaptation to evolving business demands.
- Integrates decision table, custom, and expression components, enabling flexible configuration for complex business logic, making it accessible to business users.
Together, these components create a defense framework engineered for the autonomous, iterative, and multi-step nature of agentic AI fraud, significantly reducing exposure without degrading user experience.
Conclusion
Agentic AI is transforming how digital systems operate, but it also introduces new, sophisticated fraud risks.
Autonomous agents can execute multi-step attacks, mimic human behavior, and bypass traditional security measures at scale. Businesses need layered defenses—adaptive verification, device intelligence, multi-signal behavior analysis, and robust identity controls—to disrupt these autonomous workflows and protect both users and assets.
The threat from agentic AI–driven fraud is growing rapidly. Strengthen your security strategy today with GeeTest’s adaptive, intelligence-driven solutions to detect, block, and prevent autonomous attacks before they impact your business.





