Takeaways
1. What is reCAPTCHA in 2026?
reCAPTCHA is Google’s human verification system designed to distinguish real users from bots by analyzing behavior, challenges, and risk signals across the web.
2. Is reCAPTCHA still effective against modern bots?
reCAPTCHA remains widely used, but advanced bots and AI-driven automation have reduced its effectiveness, especially in high-risk or high-traffic scenarios.
3. What is the difference between CAPTCHA and reCAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA relies on explicit human challenges, while reCAPTCHA combines challenges with behavioral and contextual risk analysis.
4. Which version of reCAPTCHA is most commonly used today?
reCAPTCHA v3 is the most deployed version in 2026 due to its frictionless, score-based verification model.
5. Are there viable alternatives to reCAPTCHA in 2026?
Yes. Modern CAPTCHA and bot management solutions, such as GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA, focus on adaptive risk defense, infrastructure-level detection, enterprise-grade SaaS services, and regional optimization.
Why reCAPTCHA Still Matters in 2026?
reCAPTCHA still matters in 2026 because automated abuse has become more scalable, adaptive, and economically damaging than ever before, while most digital businesses continue to rely on web and mobile interaction as their primary user interface.
Bots are no longer limited to simple spam scripts. Modern automated attacks include credential stuffing, fake account farms, scraping bots, scalping programs, and AI-assisted abuse that closely mimics legitimate user behavior. These threats directly affect revenue, infrastructure costs, data integrity, and user trust across industries such as SaaS, e-commerce, fintech, and online communities.
Despite rapid advances in artificial intelligence, CAPTCHA and reCAPTCHA remain relevant because many business scenarios still require an explicit or implicit mechanism to distinguish human intent from automation. In this context, reCAPTCHA continues to serve as one of the most widely deployed human verification systems, making it essential to understand how it works, where it performs well, and where its limitations become apparent in 2026.
What is reCAPTCHA?
reCAPTCHA is a human verification system that evaluates whether an interaction originates from a real person or an automated program.
It is a CAPTCHA technology developed to protect websites from bots, abuse, and automated attacks by analyzing user behavior, interaction patterns, and challenge responses.
History: From CAPTCHA → reCAPTCHA → Google reCAPTCHA
- CAPTCHA: The concept originates from CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), a general security mechanism introduced in the early 2000s to protect websites from automated abuse.
- reCAPTCHA:In 2007, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University introduced reCAPTCHA, which enhanced traditional CAPTCHA by combining security verification with large-scale data processing tasks.
- Google reCAPTCHA: In 2009, Google acquired reCAPTCHA and gradually transformed it into Google reCAPTCHA, integrating machine learning models, global traffic signals, and browser-level data. While the underlying goal remained human verification and abuse prevention, Google reCAPTCHA shifted the industry away from purely challenge-based tests toward probabilistic, behavior-driven risk assessment.
If you want to know more about CAPTCHA origin, please refer to: History of CAPTCHA – The Origin Story
CAPTCHA vs. reCAPTCHA: What’s the Difference?
CAPTCHA and reCAPTCHA share the same fundamental purpose—blocking automated abuse—but they differ significantly in how verification decisions are made and how users experience the process.
What is Traditional CAPTCHA?
Traditional CAPTCHA systems rely on explicit cognitive or perceptual tasks, such as:
- Reading distorted text
- Solving basic visual or logic puzzles
These challenges assume that humans can solve tasks that machines cannot, but this assumption has weakened as AI-based recognition has improved.
Key Differences
- User Experience: CAPTCHA introduces explicit friction, while reCAPTCHA often operates invisibly.
- Security Level: reCAPTCHA incorporates behavioral signals and global risk data beyond the challenge itself.
- Accuracy: Traditional CAPTCHA struggles with accessibility and false positives; reCAPTCHA improves accuracy through context.
- Accessibility: CAPTCHA can exclude users with visual or cognitive impairments.
- Privacy concerns: reCAPTCHA’s reliance on behavioral data introduces regulatory and privacy considerations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | CAPTCHA | reCAPTCHA |
| Interaction | Explicit challenge | Implicit + challenge |
| Friction | High | Low to moderate |
| Bot resistance | Limited | Higher |
| Accessibility | Weak | Improved |
| Privacy impact | Minimal | Higher |
Types of reCAPTCHA and How reCAPTCHA Works (v1, v2, v3)
Google reCAPTCHA has evolved through multiple versions, each reflecting changes in threat models, user experience expectations, and machine learning capabilities.
reCAPTCHA v1 (2007–2018, Deprecated)
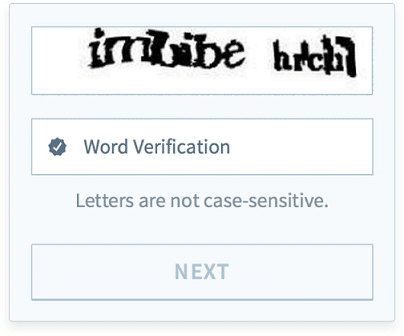
reCAPTCHA v1 was introduced as part of the original CMU project and later maintained by Google. It relied on distorted text recognition, requiring users to type words displayed in images. While effective against early bots, v1 suffered from poor usability, accessibility issues, and increasing failure rates as optical character recognition (OCR) improved.
Due to these limitations, reCAPTCHA v1 was officially deprecated in 2018.
reCAPTCHA v2 (Released in 2014)

reCAPTCHA v2 marked a major shift toward behavioral analysis combined with interactive challenges. Its most recognizable feature is the “I’m not a robot” checkbox.
When a user interacts with the checkbox, reCAPTCHA evaluates multiple signals in the background, such as mouse movement patterns, interaction timing, and browser attributes. If the risk score remains low, verification succeeds without further action. If risk is detected, users are presented with image-based challenges, such as identifying objects within a grid.
This version significantly reduced friction for many users while retaining a fallback mechanism for suspicious traffic.
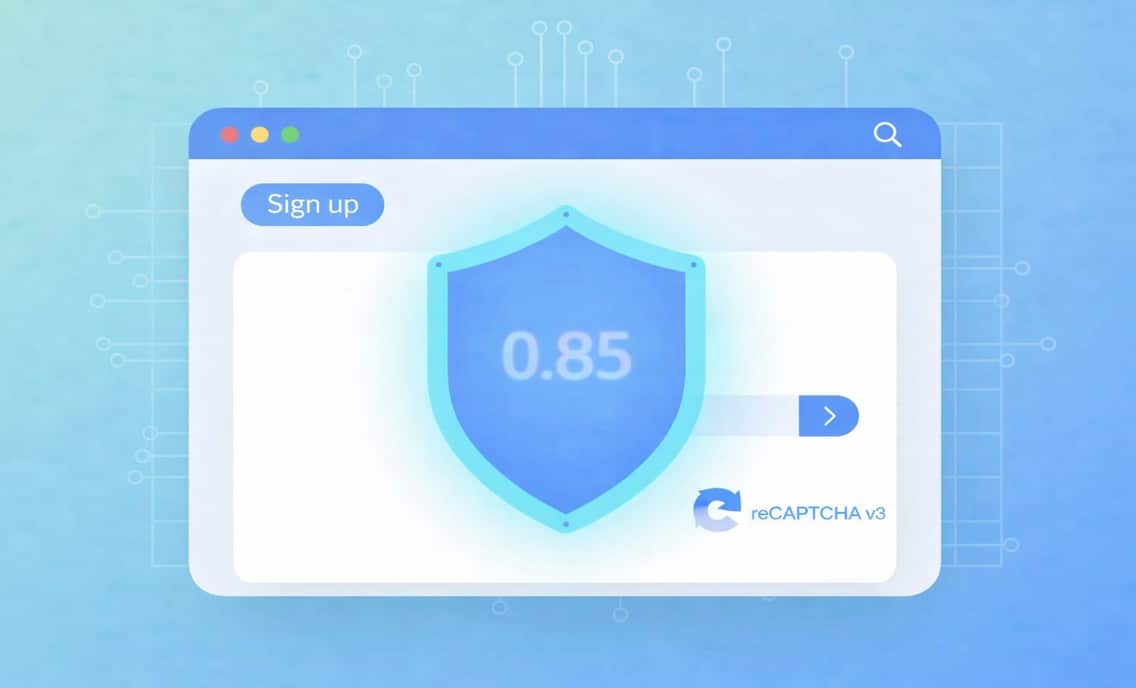
reCAPTCHA v3 (Released in 2018)

reCAPTCHA v3 removed interactive challenges entirely and introduced a continuous, score-based verification model. Every interaction generates a score between 0.0 and 1.0, representing the estimated likelihood that the interaction is human.
Instead of blocking or allowing traffic directly, reCAPTCHA v3 delegates decision-making to the website owner, who must define thresholds and responses based on score ranges. This design enables frictionless user experiences but also shifts complexity and risk management responsibilities to businesses.
In practice, reCAPTCHA v3 works by continuously collecting interaction data—such as navigation behavior, session context, and historical patterns—and processing it through machine learning models trained on large-scale web traffic.
What are the Key Features and Benefits of reCAPTCHA in 2026?
reCAPTCHA’s main benefits in 2026 are low user friction, global scalability, and ease of deployment, making it suitable for general-purpose bot protection in low-to-medium risk scenarios.
Core Features of reCAPTCHA
- Behavior-Based Human Verification: reCAPTCHA evaluates user interactions—such as mouse movements, click patterns, and session behavior—to infer whether traffic is human or automated, reducing reliance on explicit challenges.
- Multiple Verification Modes: Through v2 and v3, reCAPTCHA supports both challenge-based verification and invisible, score-based risk assessment, allowing websites to choose different interaction models.
- Global Infrastructure and Availability: Backed by Google’s infrastructure, reCAPTCHA operates reliably across regions and can handle large traffic volumes without additional configuration.
- Easy Integration and Maintenance: Standard APIs and minimal setup make reCAPTCHA easy to integrate, especially for teams with limited security engineering resources.
These advantages explain why reCAPTCHA remains widely adopted despite growing limitations.
What are the Limitations and Drawbacks of reCAPTCHA (Especially v3)?
reCAPTCHA’s limitations in 2026 mainly stem from its opaque scoring logic, limited controllability, and misalignment with enterprise-grade risk management needs.
Structural Limitations of reCAPTCHA v3
- Black-Box Risk Scoring: reCAPTCHA v3 provides a numeric score without explaining which signals influenced the result, making it difficult to audit, troubleshoot, or justify decisions.
- Challenging Threshold Management: Businesses must define score thresholds themselves, yet optimal thresholds vary by scenario, traffic source, and time. Improper tuning often leads to false positives or missed attacks.
- Limited Decision Capability: reCAPTCHA supplies a signal, not a decision. Enterprises still need to build additional logic to determine whether to block, challenge, or allow a request.
Operational and Compliance Concerns
- Difficulty explaining decisions to internal stakeholders
- Potential privacy and data residency considerations
- Limited adaptability to highly dynamic or industry-specific threats
As a result, reCAPTCHA is often insufficient as a standalone solution in complex environments.
What Are the Most Common Use Cases for Google reCAPTCHA?
Google reCAPTCHA is most effective in standardized, low-to-medium risk scenarios where the primary goal is to block generic automated traffic rather than perform complex, business-aware risk decisions.
Typical Use Cases
User Registration and Login Protection: reCAPTCHA helps reduce automated account creation, credential stuffing attempts, and basic brute-force attacks.
Forms, Surveys, and Feedback Channels: Contact forms and surveys are frequent spam targets, and reCAPTCHA provides a simple, low-cost barrier against automated submissions.
Comment Systems and Community Platforms: For blogs, forums, and content platforms, reCAPTCHA reduces low-effort bot comments without heavily impacting user experience.
Low-Risk Transaction Checkpoints: In scenarios where a single verification signal is sufficient, reCAPTCHA adds an extra layer of protection without complicating the workflow.
Where These Use Cases Start to Break Down
reCAPTCHA use cases begin to break down when verification requires differentiated treatment, business context, and dynamic control rather than uniform bot filtering.
1. Different Users Carry Different Levels of Risk
Not all users should face the same verification logic.
- New users vs. returning users
- High-value accounts vs. anonymous traffic
- Trusted regions vs. high-risk sources
Uniform scoring makes it difficult to apply differentiated protection.
2. Business Scenarios Require Context-Aware Decisions
Different actions involve different risk profiles.
- Registration, login, promotions, and payments vary significantly
- One global verification strategy cannot fit all scenarios
- Business intent is not reflected in static challenges
This limits precision in real-world applications.
3. Attacks Are Event-Driven and Adaptive
Modern abuse often spikes during specific business events.
- Marketing campaigns
- Flash sales and promotions
- Feature launches
Static thresholds struggle to respond fast enough.
4. Enterprises Need Control and Explainability
Large organizations require visibility and governance.
- Clear reasoning behind challenge or block decisions
- Adjustable rules aligned with internal policies
- Auditability for risk and compliance teams
Opaque scoring models reduce operational control.
What Are the Best Alternatives to reCAPTCHA in 2026?
In 2026, the most effective alternatives to reCAPTCHA no longer rely on one-size-fits-all challenges, but instead focus on adaptive verification, enterprise-grade services, and scenario-based risk protection.
Key Alternative Approaches
1. Adaptive Verification Instead of Static Challenges
Verification intensity adjusts dynamically based on risk.
- Low-risk users pass with minimal friction
- Suspicious behavior triggers stronger verification
- Real-time signals replace fixed rules
This improves both security accuracy and user experience.
2. Enterprise Services Beyond Basic CAPTCHA
Modern solutions extend beyond technical verification.
- Enterprise onboarding and integration support
- Ongoing risk strategy optimization
- Dedicated service and response mechanisms
CAPTCHA becomes part of a broader risk system.
3. Scenario-Based Risk Protection Rather Than Uniform Scoring
Verification logic aligns with business context.
- Different strategies for different user actions
- Risk decisions tied to specific scenarios
- Behavioral and contextual signals combined
This enables fine-grained, business-aligned protection.
Recommended Enterprise Solution: GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA
GeeTest Adaptive CAPTCHA follows these modern principles by offering adaptive verification, enterprise-level services, and scenario-based risk protection in a unified solution.
- Adaptive verification: Verification strength adjusts in real time based on risk, reducing friction for legitimate users while escalating protection for abnormal behavior.
- Scenario-based protection: Different business flows—such as registration, login, promotions, and transactions—can apply different verification strategies instead of a single global rule.
- Enterprise-grade control and services: Supports large-scale traffic, configurable risk logic, and professional service support suited for complex, high-risk business environments.
By focusing on adaptability, scenario precision, and enterprise operability, GeeTest provides a more practical alternative to traditional reCAPTCHA deployments in 2026.
Conclusion: Is reCAPTCHA Still the Right Choice in 2026?
reCAPTCHA remains a practical solution in 2026 for basic bot protection and low-risk use cases, but it is no longer sufficient for every business scenario.
Organizations should evaluate reCAPTCHA based on their risk complexity, compliance requirements, and need for decision transparency. For enterprises facing evolving threats and dynamic business rules, more adaptive and controllable CAPTCHA solutions are increasingly necessary.